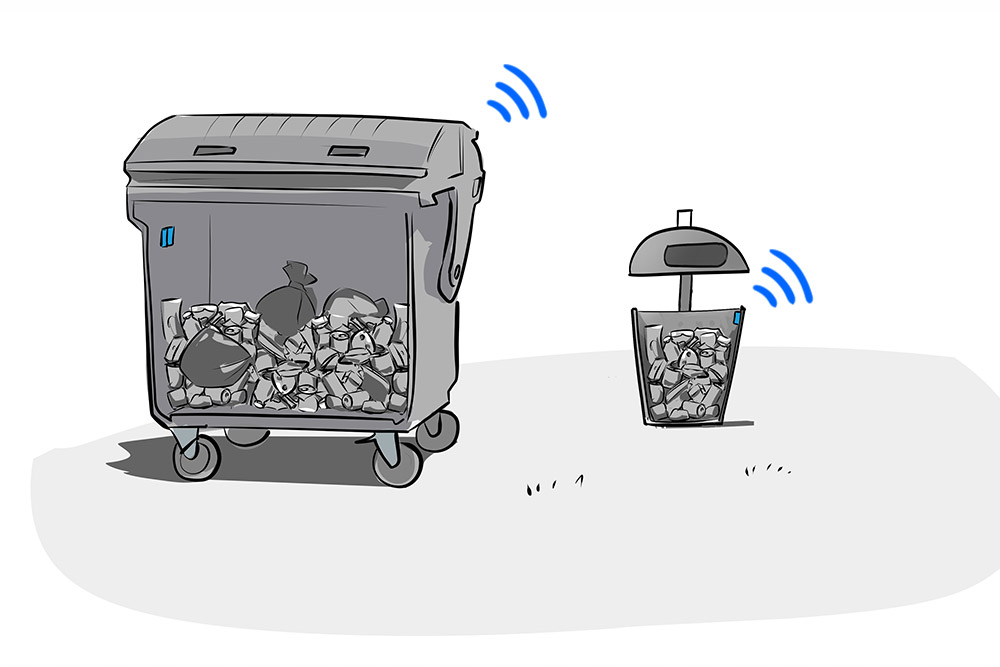
Clean air is particularly important to the citizens of Wuppertal. Wuppertal’s municipal utilities now want to make a contribution to this with an IoT project. In future, all recycling containers will be emptied route-optimised and based on fill level, which will reduce emissions and costs.
With Smart Waste against NO2 Pollution
Internet of Things (IoT) projects for the digitalisation of municipal processes usually enjoy a high level of acceptance among all stakeholders. This is largely due to the fact that a large and sustainable benefit is generated for all parties involved with a manageable investment, which would not be possible without the use of the new technology.
The joint Smart Waste project of Abfallwirtschaftsgesellschaft mbH (AWG) and Wuppertaler Stadtwerke GmbH (WSW) is a clear example of this. There are depot containers for the recyclable materials paper, glass, used clothing and small electrical appliances at 441 public locations in the city.
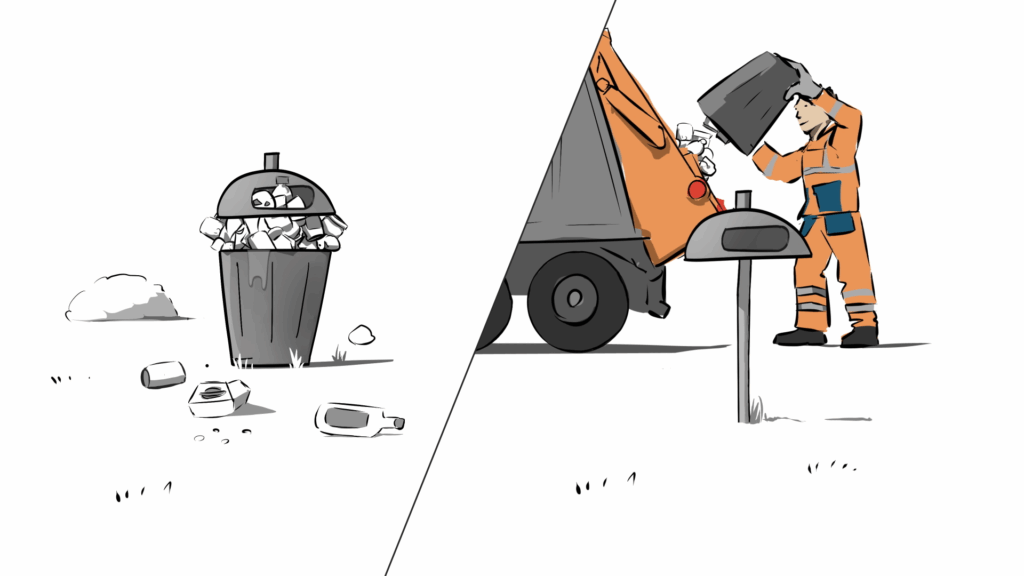
These are currently approached and emptied by the AWG at fixed intervals. The disadvantages of calendar-based emptying are obvious: At particularly frequented locations, the bins are often full before the emptying date, so that recyclables are sometimes deposited in front of them or citizens have to go to other locations.
Other containers, on the other hand, still have plenty of capacity at the turnaround date. If they were emptied according to demand, i.e. depending on the actual fill level, it would be possible both to avoid clutter in overfilled containers and – particularly important in Wuppertal – to reduce the number of kilometres driven by the AWG vehicle fleet and thus reduce nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions in the urban area.
Tool for smart city projects
When the WSW employees visited the ZENNER Group’s stand at E-World 2020 to find out about the possibilities of digitalisation, they quickly realised that the IoT standard LoRaWAN as a tool for implementing digital smart city projects could also become a lever for reducing NO2 emissions. That’s why they were one of the first to tackle the Smart Waste project. The live data is provided by LoRaWAN level sensors installed in the containers. IoT gateways distributed throughout the city collect the level data from the sensors and forward it to the backend system. All LoRaWAN-based data traffic is encrypted.
The ELEMENT IoT platform developed by ZENNER brings together all the data that is sent through the gateways. WSW developed its own backend system that receives data from the ELEMENT platform in real time, generates valuable information from it and processes it. In addition to fill level monitoring, this can also be used to calculate flexible route planning for the collection of recyclables, which makes this digitalisation project particularly sustainable.

Project experiences give reason to be confident
The project started with technical tests: Which sensors are suitable? How is the range and connectivity of the sensors and IoT gateways on site? Based on the results, ZENNER and WSW conceptualised and rolled out the IoT network. At the same time, WSW developed the dashboard for route planning. After extensive testing, the entire IoT system is now in operation – initially for all glass containers in the city.
Markus Hilkenbach, Chairman of the WSW Management Board, explains: “The establishment of a comprehensive LoRaWAN infrastructure in Wuppertal enables us to implement various use cases within the WSW Group and, in future, for external customers as well. Together with AWG, we are now digitising the fill levels within the depot containers, starting with the glass containers. On this basis, we optimise route planning with the aim of saving costs and making a contribution to reducing NO2 in the urban area. We are successfully using the LoRa network server from ZENNER.”
IoT network can be used for other applications
Other LoRaWAN-based applications at WSW include remotely readable heat meters in the district heating network and the provision of status information from the medium-voltage network. Pilot projects are also planned in the areas of CO2 measurement, submetering and demand-based control of street lighting. Advantageous: The existing LoRaWAN radio network can be used for these and other applications. ZENNER already has solutions and extensive project experience in all these fields, some of which have been developed with partners and customers.
Nevertheless, the Smart Waste project in Wuppertal is not an off-the-peg project: “It is particularly interesting for us because the smart waste use case is being rolled out there on a rarely large scale,” comments René Claussen, Head of IoT & Digital Solutions at ZENNER. “This also means specific new learning effects for us, which we will incorporate into future projects.”

The Smart Waste project in Wuppertal contributes to the following UN goals: